How to Build Corva Frontend Apps with Highcharts - Complete Guide
What You'll Build
In this guide, you'll learn how to build Corva frontend applications with Highcharts integration for powerful data visualization. You'll create a real-time drilling data visualization app that displays WITS (Wellsite Information Transfer Specification) data using interactive Highcharts. The app will show drilling parameters like hole depth updated in real-time, demonstrating the complete workflow of building Corva FE apps with advanced charting capabilities.
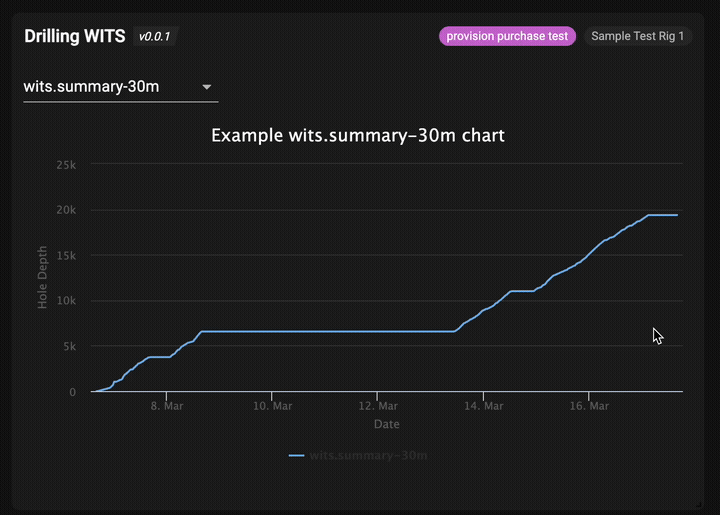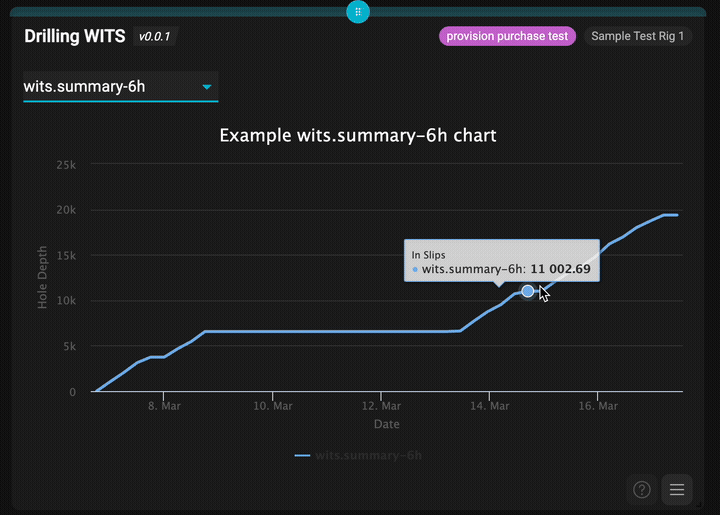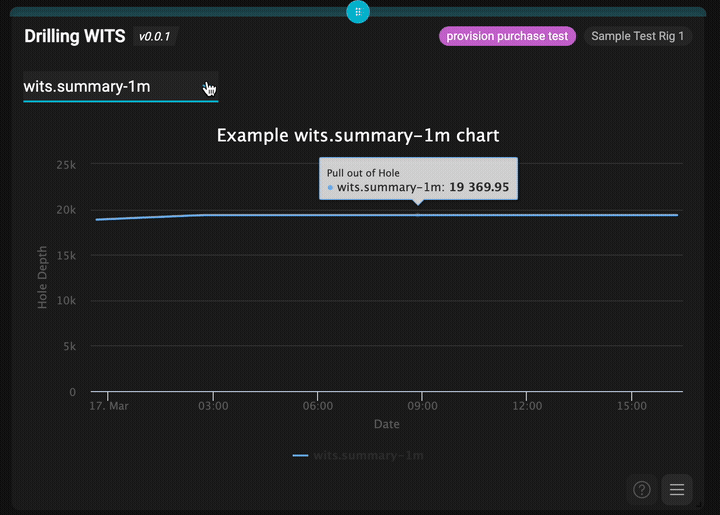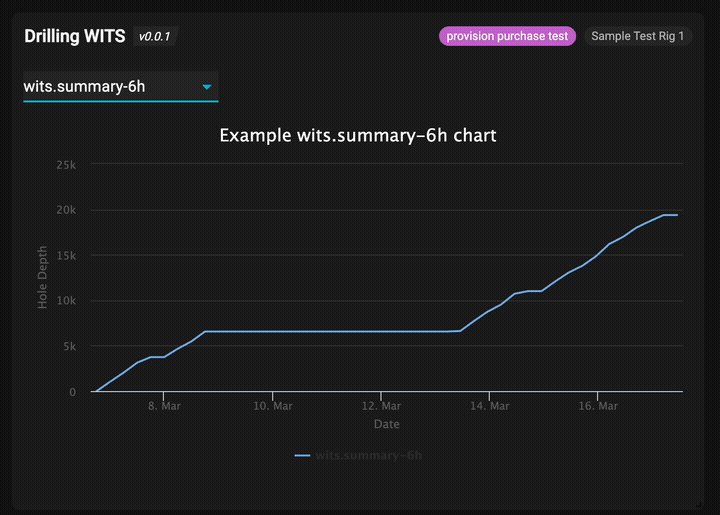
The completed drilling WITS app showing real-time data visualization
Key Features You'll Implement:
- ✅ Real-time drilling data visualization
- ✅ Interactive Highcharts integration
- ✅ Multiple time interval selection (6h, 30m, 1m, 1ft)
- ✅ Responsive modern UI using Corva Design System
- ✅ Live data streaming via Corva SDK
Prerequisites
System Requirements
- Node.js: Version 18 or higher (required for @corva/ui 3.12.0+)
- Yarn: Package manager
- Git: Version control
- Corva Account: Access to Corva platform
Verify Your Environment
# Check Node version (should be 18+)
node --version
# Check if yarn is installed
yarn --version
# Install yarn if needed
npm install -g yarn
If you need Node 18, use nvm:
# Install nvm if needed
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.0/install.sh | bash
# Install and use Node 18
nvm install 18
nvm use 18
Step 1: Generate the Base App Using Corva CLI
Create your new drilling WITS app using the Corva CLI:
npx @corva/create-app drilling-wits-app \
--appName "Drilling WITS Dashboard" \
--segments "drilling" \
--category "analytics" \
--appKey "your-company.drilling_wits_dashboard.ui" \
--appType "ui" \
--runtime "ui"
This command creates a basic React app structure with these files:
# Navigate to your new app
cd drilling-wits-app
# Install dependencies
yarn install
Step 2: Understanding the Generated App Structure
After generation, your project structure looks like this:
drilling-wits-app/
├── src/
│ ├── App.js # Basic component showing rig/well info
│ ├── AppSettings.js # Simple settings with checkbox
│ ├── constants.js # Basic default settings
│ ├── index.js # App entry point
│ ├── App.css # Basic styling
│ └── assets/ # Static assets (logo, etc.)
├── config-overrides.js # Webpack configuration
├── package.json # Dependencies and scripts
├── manifest.json # Corva app manifest
├── .nvmrc # Node version specification
├── .eslintrc # ESLint configuration
└── README.md # Project documentation
Generated Files Explained:
src/App.js - Basic component that displays rig and well information:
// Generated basic App.js
function App({ isExampleCheckboxChecked, rig, well }) {
return (
<AppContainer header={<AppHeader />}>
<div>
<img src={logo} alt="logo" />
<p>Rig: {rig.name}</p>
<p>Well: {well.name}</p>
<p>Settings checkbox is {isExampleCheckboxChecked ? 'checked' : 'unchecked'}</p>
</div>
</AppContainer>
);
}
src/AppSettings.js - Simple settings component with one checkbox:
// Generated basic AppSettings.js
function AppSettings({ settings, onSettingChange }) {
return (
<div>
<FormControlLabel
label="Example checkbox"
control={
<Checkbox
checked={settings.isExampleCheckboxChecked}
onChange={e => onSettingChange('isExampleCheckboxChecked', e.target.checked)}
/>
}
/>
</div>
);
}
src/constants.js - Basic default settings:
// Generated basic constants.js
export const DEFAULT_SETTINGS = {
isExampleCheckboxChecked: false,
};
Step 3: Install Additional Dependencies for WITS Visualization
Add the required packages for data visualization and real-time functionality:
yarn add highcharts highcharts-react-official lodash prop-types
Important: Currently, the maximum supported Highcharts version is 8.1.2. Support for higher versions will be added in future releases.
Update your package.json to match our target configuration:
{
"name": "DrillingWITS",
"version": "0.0.1",
"main": "src/index.js",
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack --config=./config-overrides.js --mode production",
"start": "webpack-dev-server --config=./config-overrides.js --open --mode development",
"zip": "create-corva-app --zip ui",
"lint": "eslint --cache ./src/"
},
"dependencies": {
"@corva/ui": "^3.12.0",
"@material-ui/core": "4.11.2",
"@material-ui/icons": "4.9.1",
"@material-ui/lab": "4.0.0-alpha.57",
"@material-ui/pickers": "3.2.10",
"classnames": "2.2.6",
"corva-convert-units": "1.10.33",
"highcharts": "8.1.2",
"highcharts-react-official": "2.2.2",
"lodash": "^4.17.21",
"mapbox.js": "3.2.1",
"moment": "2.29.4",
"moment-timezone": "0.5.43",
"prop-types": "^15.6.1",
"react": "17.0.1",
"react-dom": "17.0.1"
},
"devDependencies": {
"postcss-loader": "4.2.0",
"webpack": "5.94.0",
"webpack-dev-server": "4.15.2",
"webpack-cli": "5.1.4",
"@corva/dc-platform-shared": "latest",
"babel-loader": "8.1.0",
"@babel/core": "^7.12.10",
"@babel/preset-env": "^7.12.11",
"@babel/preset-react": "^7.12.10",
"postcss": "8.4.31"
}
}
Step 4: Transform Constants for WITS Data
Replace the basic constants with WITS-specific dataset definitions:
Replace src/constants.js:
export const DATASETS = [
'wits.summary-6h',
'wits.summary-30m',
'wits.summary-1m',
'wits.summary-1ft',
];
These represent different time intervals for WITS data aggregation, allowing users to view drilling data at various granularities.
Step 5: Create the Data Fetching Hook
Create a new directory structure and build a custom React hook for WITS data management:
Create directory: src/effects/
Create src/effects/useWITSSummaryData.js:
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { corvaDataAPI, socketClient } from '@corva/ui/clients';
import { reverse } from 'lodash';
async function fetchWITSSummaryData({ assetId, dataset }) {
try {
return await corvaDataAPI.get(`/api/v1/data/corva/${dataset}/`, {
limit: 1000,
skip: 0, // NOTE: Required for pagination
// NOTE: Make sure the sort field hit database indexes. Otherwise the request will take too long
sort: JSON.stringify({ timestamp: -1 }),
query: JSON.stringify({ asset_id: assetId }),
// NOTE: To make efficient request - fetch only fields used by the app
fields: ['timestamp', 'data.hole_depth', 'data.state'].join(','),
});
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
return [];
}
}
function useWITSSummaryData({ assetId, dataset }) {
// NOTE: Define state to store subscription data
const [witsSummaryData, setWITSSummaryData] = useState([]);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
let unsubscribe;
setLoading(true);
// Make initial request first
fetchWITSSummaryData({ assetId, dataset })
.then(response => {
setWITSSummaryData(reverse(response));
const subscription = { provider: 'corva', dataset, assetId }; // Subscription params
// Concatenate new records to state
const onDataReceive = event => setWITSSummaryData(prevData => prevData.concat(event.data));
// NOTE: Subscribe to updates after initial data request
unsubscribe = socketClient.subscribe(subscription, { onDataReceive });
})
.finally(() => setLoading(false));
// NOTE: Unsubscribe to prevent memory leaks and crashes in your app.
return () => unsubscribe?.();
}, [assetId, dataset]);
return { loading, witsSummaryData };
}
export default useWITSSummaryData;
Create src/effects/index.js:
export { default as useWITSSummaryData } from './useWITSSummaryData';
How This Hook Works:
- Initial HTTP Request: Fetches the last 1000 WITS records for the selected dataset
- WebSocket Subscription: Establishes real-time connection for live updates
- State Management: Manages loading states and data updates
- Memory Management: Properly cleans up subscriptions to prevent leaks
Step 6: Build the Chart Component System
Create the Highcharts integration components:
Create directory: src/components/WITSSummaryChart/
Create src/components/WITSSummaryChart/options.js:
const defaultHighchartsOptions = {
chart: {
backgroundColor: '#201f1f',
type: 'line',
},
plotOptions: {
series: {
marker: {
enabled: false,
},
},
},
xAxis: {
type: 'datetime',
title: { text: 'Date' },
},
yAxis: {
title: { text: 'Hole Depth' },
gridLineColor: '#3b3b3b',
min: 0,
},
credits: { enabled: false },
exporting: { enabled: false },
};
export function getHighchartsOptions({ data, dataset }) {
const series = [
{
name: dataset,
data: data.map(witsRecord => ({
x: witsRecord.timestamp * 1000,
y: witsRecord.data.hole_depth,
name: witsRecord.data.state,
})),
turboThreshold: 20000,
},
];
return {
...defaultHighchartsOptions,
title: { text: `Example ${dataset} chart`, style: { color: 'white' } },
series,
};
}
Create src/components/WITSSummaryChart/index.js:
import { useMemo, useRef, useEffect } from 'react';
import Highcharts from 'highcharts';
import HighchartsReact from 'highcharts-react-official';
import { getHighchartsOptions } from './options';
import styles from './styles.css';
function WITSSummaryChart({ data, dataset, coordinates }) {
const chartRef = useRef();
useEffect(() => {
// NOTE: Update chart size when container size has changed
chartRef.current?.chart.setSize();
}, [coordinates]);
// NOTE: Use memoization technique
// Calculate chart options ONLY when data changed.
// This will also help avoid choppy animation
return useMemo(() => {
const options = getHighchartsOptions({ data, dataset });
return (
<HighchartsReact
highcharts={Highcharts}
options={options}
// NOTE: Pass className to style highchart
containerProps={{ className: styles.chartContainer }}
ref={chartRef}
/>
);
}, [data]);
}
export default WITSSummaryChart;
Create src/components/WITSSummaryChart/styles.css:
.chartContainer {
height: 400px;
width: 100%;
margin: 20px 0;
}
Create src/components/index.js:
export { default as WITSSummaryChart } from './WITSSummaryChart';
Step 7: Transform the Main App Component
Replace the basic generated App.js with our sophisticated drilling visualization interface:
Replace src/App.js:
/*
This example is a simple app which consists of: AppHeader, Select and Highcharts Chart
*/
import { useState } from 'react';
import { LoadingIndicator, AppHeader, Select } from '@corva/ui/components';
import { MenuItem } from '@material-ui/core';
import { useWITSSummaryData } from './effects';
import { WITSSummaryChart } from './components';
import { DATASETS } from './constants';
import styles from './styles.css';
function App(props) {
// NOTE: Read asset_id from well. Most datasets are indexed by asset_id.
const {
well: { asset_id: assetId },
coordinates,
appHeaderProps,
} = props;
const [dataset, setDataset] = useState(DATASETS[0]);
// NOTE: Use custom react hook to encapsulate data fetching/subscriptions logic
const { witsSummaryData, loading } = useWITSSummaryData({ assetId, dataset });
return (
<div className={styles.container}>
<AppHeader {...appHeaderProps} />
<div className={styles.content}>
<Select
value={dataset}
onChange={e => setDataset(e.target.value)}
FormControlProps={{ className: styles.select }}
>
{DATASETS.map(dataset => (
<MenuItem key={dataset} value={dataset}>
{dataset}
</MenuItem>
))}
</Select>
{/*Show loading indicator while data is loading*/}
{loading && <LoadingIndicator />}
{!loading && (
<WITSSummaryChart data={witsSummaryData} coordinates={coordinates} dataset={dataset} />
)}
</div>
</div>
);
}
// Important: Do not change root component default export (App.js). Use it as container
// for your App. It's required to make build and zip scripts work as expected;
export default App;
Key Transformations Made:
- Removed basic rig/well display → Added sophisticated data visualization
- Added dataset selection → Dropdown for choosing time intervals
- Integrated custom hook → Real-time data fetching and management
- Added chart component → Highcharts visualization
- Enhanced layout → Professional container and content structure
Step 8: Add Professional Styling
Create new styling to replace the basic generated styles:
Create src/styles.css:
.container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
height: 100%;
background-color: #1a1a1a;
}
.content {
flex: 1;
padding: 20px;
overflow: auto;
}
.select {
margin-bottom: 20px;
min-width: 200px;
}
Update src/App.css:
.App {
text-align: center;
background-color: #1a1a1a;
color: white;
min-height: 100vh;
}
.App-header {
background-color: #282c34;
padding: 20px;
color: white;
}
.App-link {
color: #61dafb;
}
/* Additional styling for drilling app */
.drilling-container {
padding: 20px;
max-width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.dataset-selector {
margin-bottom: 20px;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 10px;
}
.chart-wrapper {
background-color: #2a2a2a;
border-radius: 8px;
padding: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
}
Step 9: Update App Settings
Transform the basic settings to work with our drilling app:
Replace src/AppSettings.js:
import { Checkbox, FormControlLabel } from '@material-ui/core';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
import { DATASETS } from './constants';
function AppSettings({
settings: apiSettings,
onSettingChange,
// appData,
// app,
// user,
// company,
}) {
const settings = { ...DATASETS, ...apiSettings };
return (
<div>
<FormControlLabel
label="Example checkbox"
control={
<Checkbox
checked={settings.isExampleCheckboxChecked}
onChange={e => onSettingChange('isExampleCheckboxChecked', e.target.checked)}
/>
}
/>
</div>
);
}
AppSettings.propTypes = {
app: PropTypes.shape({}).isRequired,
appData: PropTypes.shape({}).isRequired,
company: PropTypes.shape({}),
onSettingChange: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
settings: PropTypes.shape({
isExampleCheckboxChecked: PropTypes.bool
}).isRequired,
user: PropTypes.shape({}),
};
AppSettings.defaultProps = {
user: {},
company: {},
};
// Important: Do not change root component default export (AppSettings.js). Use it as container
// for your App Settings. It's required to make build and zip scripts work as expected;
export default AppSettings;
Step 10: Test Your Transformed Application
Start the development server to see your transformation:
yarn start
What You Should See:
- Dataset Selection: Dropdown with WITS time intervals (6h, 30m, 1m, 1ft)
- Loading States: Professional loading indicators during data fetch
- Real-time Chart: Highcharts visualization showing hole depth over time
- Responsive Design: Chart adjusts to window size changes
Testing Your App:
- Dataset Selection: Switch between different time intervals
- Loading States: Verify loading indicators appear during data fetch
- Real-time Updates: Check browser console for WebSocket connections
- Chart Visualization: Confirm hole depth data displays correctly
- Responsive Design: Resize browser window to test chart responsiveness
Debugging:
- Console Logs: Check for API call logs and WebSocket connection status
- Network Tab: Monitor HTTP requests to
/api/v1/data/corva/{dataset}/ - Data Verification: Ensure asset_id is being extracted from well context
Step 11: Understanding the Complete Data Flow
How Everything Works Together:
App Initialization:
- Component mounts and extracts
asset_idfrom well props - Sets initial dataset to first option (6h)
- Component mounts and extracts
Data Fetching Hook Activation:
useWITSSummaryDatahook triggers with asset ID and dataset- Makes HTTP request to
/api/v1/data/corva/wits.summary-6h/ - Fetches last 1000 records with optimized field selection
Initial Data Processing:
- Response data is reversed (oldest first for time series)
- Loading state is set to false
- Chart component receives data
WebSocket Subscription:
- Real-time subscription established for live updates
- New data automatically appends to existing dataset
- Chart updates in real-time
Chart Rendering:
- Highcharts transforms WITS data into time series format
- Displays hole depth over time with professional styling
- Memoization prevents unnecessary re-renders
User Interactions:
- Dataset selection triggers new API calls
- Loading states provide user feedback
- Chart updates with new time interval data
API Endpoints Used:
- HTTP:
/api/v1/data/corva/wits.summary-{interval}/for initial data - WebSocket: Real-time subscription for live drilling data updates
Data Structure:
// WITS record structure
{
timestamp: 1640995200,
asset_id: "drilling-rig-123",
data: {
hole_depth: 1250.5,
state: "drilling"
}
}
Step 12: Build and Deploy
Create Production Build:
yarn build
Package for Deployment:
yarn zip
Deploy to Corva Platform:
yarn release
Your complete drilling WITS visualization app will be available in the Corva platform's drilling segment.
Step 13: Summary of Transformation
What We Changed:
From Basic Generated App:
- Simple rig/well display
- Basic checkbox setting
- Static content
- Minimal styling
To Sophisticated WITS App:
- Real-time data visualization
- Multiple dataset selection
- Custom React hooks for data management
- Highcharts integration
- Professional UI with loading states
- WebSocket subscriptions for live updates
Files Added/Modified:
New Files:
src/effects/useWITSSummaryData.js- Custom data hooksrc/effects/index.js- Effects exportsrc/components/WITSSummaryChart/index.js- Chart componentsrc/components/WITSSummaryChart/options.js- Chart configurationsrc/components/WITSSummaryChart/styles.css- Chart stylingsrc/components/index.js- Components exportsrc/styles.css- App styling
Modified Files:
src/App.js- Complete transformation to data visualizationsrc/constants.js- WITS datasets instead of basic settingssrc/AppSettings.js- Updated with PropTypessrc/App.css- Enhanced stylingpackage.json- Added visualization dependencies
This transformation demonstrates how to evolve a basic Corva app into a sophisticated, production-ready drilling data visualization application with real-time capabilities.